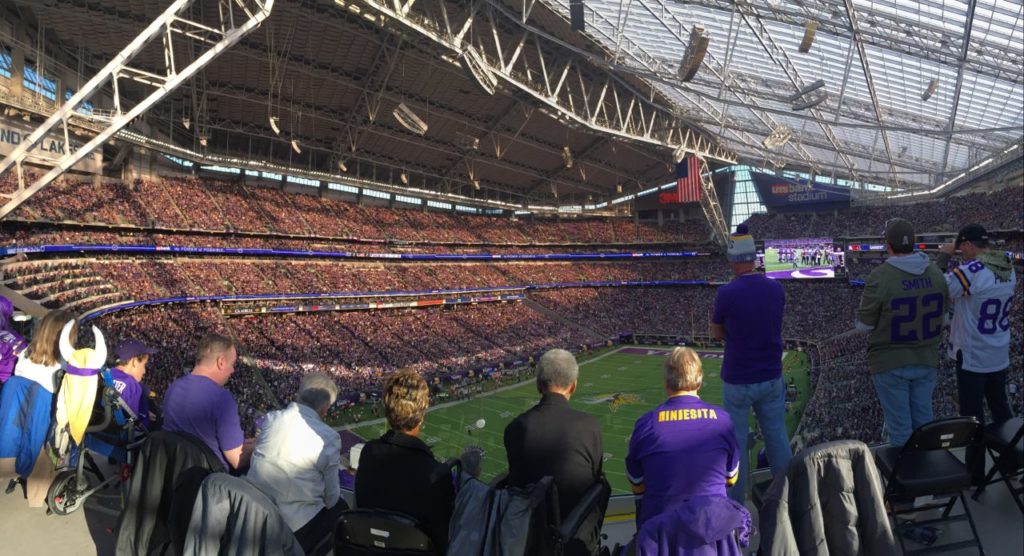
The video board shows team captains assembling before kickoff at last week’s playoff game between the Vikings and Niners at Levi’s Stadium. Credit: Brian Nitenson, MSR (click on any picture for a larger image)
While that mark may eventually be eclipsed at this weekend’s NFL Championship game against the visiting Green Bay Packers, the packed house of 71,649 fans who witnessed the Niners’ 27-10 victory over the visiting Minnesota Vikings spent a lot of time using the stadium’s Wi-Fi network, with 21,195 unique connections recorded by the Niners. The peak concurrent connection number was 15,075, according to the Niners.
Of all the big events at Levi’s Stadium since its opening in 2014, only Super Bowl 50 on Feb. 7, 2016, saw more Wi-Fi used by fans, with 10.1 TB used that day. Last January, a crowd of 74,814 attending the college football playoff championship game between Alabama and Clemson used 5.1 TB of Wi-Fi data, the previous No. 2 mark at Levi’s. Other big-event totals included 4.5 TB used during Wrestlemania 31 on March 29, 2015 (with 76,976 fans in attendance).
DAS also strong
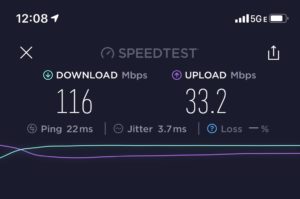
While Levi’s Stadium still has the original number of approximately 1,300 Aruba Wi-Fi APs as the opening-day design, the cellular distributed antenna network (DAS) has undergone additions and improvements almost since the venue opened, including a significant upgrade from Verizon ahead of Super Bowl 50. Though we don’t have an exact count yet of the total of DAS antennas in the stadium, from visits over the past few years MSR has seen more DAS antennas each time we’ve visited, no surprise since the bandwidth demands from fans continue to increase.MSR contributing editor Keith Newman was at Sunday’s game and got strong DAS speed tests on the main concourse and on the stadium’s top levels, in the 30 Mbps range each time. On the press box level on Levi’s Stadium’s west side, he got a mark of 116 Mbps on the download and 33.2 Mbps on the upload.
Below, some more photos from our field team at Sunday’s game. If you are at the championship game this week, send us some pix and speedtests!
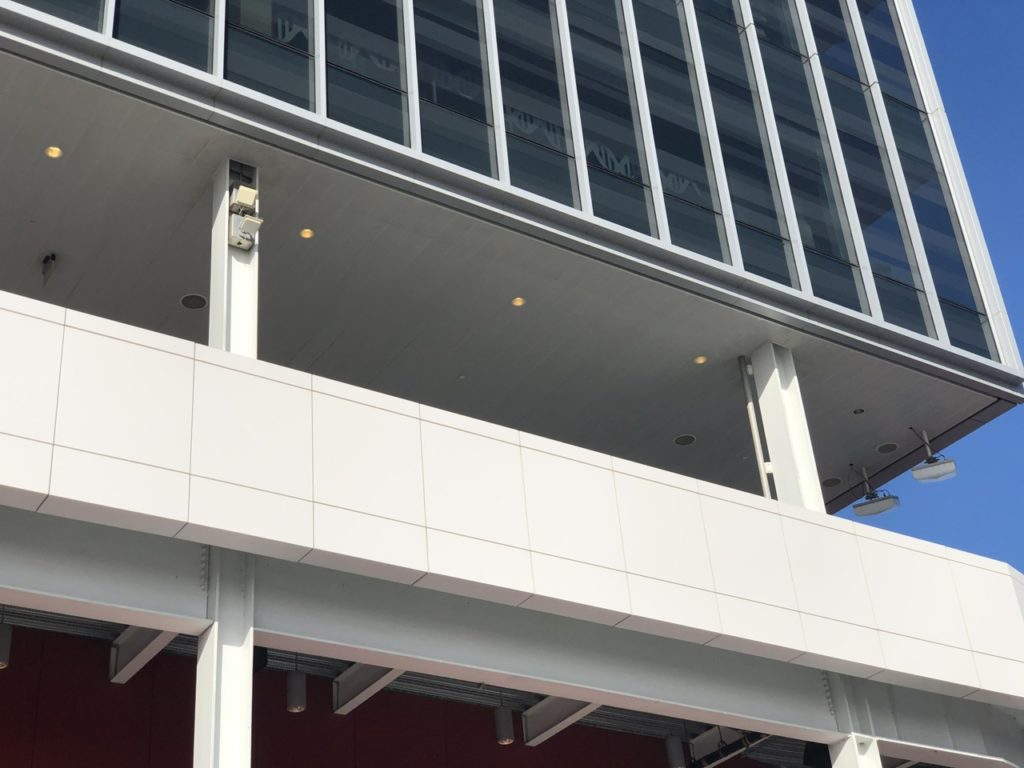
Wi-Fi and DAS antennas visible on the stadium structures. Credit: Keith Newman, MSR
Niners fans getting their tailgate on before the game. Credit: Brian Nitenson, MSR