A legendary telecom building in downtown Los Angeles, the city that was the home of last week’s Mobile World Congress Americas show. Credit all photos: Paul Kapustka, MSR (click on any picture for a larger image)
At Angel Stadium in nearby Anaheim, a group of companies led by Connectivity Wireless and JMA teamed up to do some live demonstrations of use cases for the CBRS spectrum, a swath of 150 MHz in the 3.5 GHz range that uses the cellular LTE standard for device communications. One demo we heard about reportedly used a Motorola push-to-talk (PTT) handset to carry on a conversation from a suite behind home plate to centerfield, a “home run” distance of at least 400 feet.
Mobile Sports Report, which doesn’t often attend trade shows, found lots for venue technology professionals to be interested in at the show, including the live demonstrations of CBRS-connected devices in the JMA booth that included handsets, headsets and standalone digital displays using CBRS for back-end connectivity. MSR also sat down with Heidi Hemmer, Verizon’s vice president of technology, to talk about 5G for stadiums and why the push for the new cellular standard doesn’t mean the end of Wi-Fi. Read on for highlights of our visit to LA, which also included an interview with Boingo’s new CEO Mike Finley and with Paul Challoner, a CBRS expert at Ericsson.
Look at me, I can hear… centerfield
MSR wasn’t able to make it to the press event held at Angel Stadium, but we heard from multiple sources that the trial CBRS network installed there for a short stint in October by Connectivity Wireless and JMA performed as advertised, especially with the aforementioned full-field PTT talk between two devices, with one of those more than 400 feet away from the CBRS radio.
Thanks to @ConnectivityWS and @JMAwireless for an awesome event at Angel Stadium last night! Exciting things happening with #CBRS. pic.twitter.com/SoVab7fudU
— Inside Towers (@InsideTowers) October 22, 2019
The worth of the ability for a device to communicate to a access-point radio at such a distance should be clearly apparent to venue wireless professionals, who may want to tap into CBRS networks to increase connectivity inside their venues. With more powerful radios than Wi-Fi and connectivity that utilizes the mobility and security of the LTE standard, teams and venues may look to CBRS for back-of-house communications that would benefit from being separated from the shared Wi-Fi infrastructures. While we are still waiting for the first publicly announced contract win for CBRS in venues — even the Angels are still weighing the decision to go forward with a CBRS deal — being able to show networks working live is a big step forward in the “is it real” phase.
Connecting digital displays, and more PTT
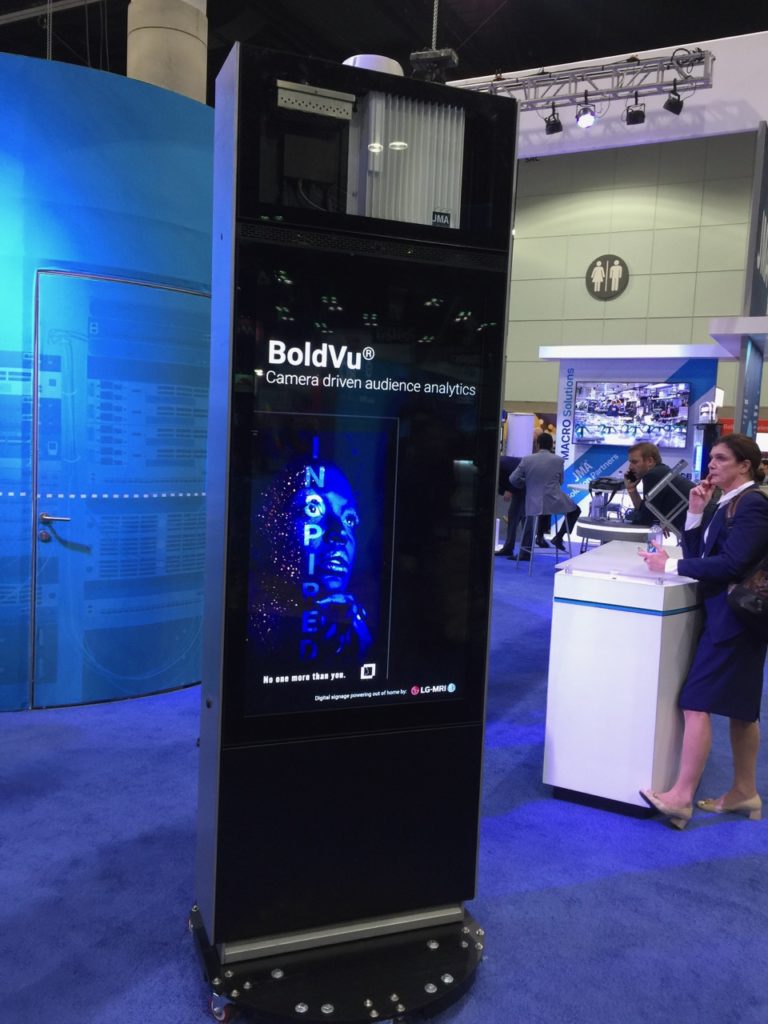
If there was a true “hot spot” for CBRS activity on the MWC show floor, it was at the JMA booth, where the wireless infrastructure company was running a live CBRS network with all kinds of devices running off it. JMA, which was showing its own CBRS radio cell (a kind of access point-on-steroids radio that will provide connectivity to client devices in a CBRS network) as well as a version of its XRAN virtual network core software, had a working prototype of one of the first commercially announced CBRS networks, a wireless deployment of digital displays for the parking lots at the American Dream shopping mall in New Jersey.

A prototype of the CBRS-connected displays JMA is installing at the American Dream mall. (Don’t miss the Jimmy Hoffa joke at the bottom)
But after considering a traditional deployment with fiber backhaul and Wi-Fi — which Jacobs said would have cost the mall at least $3 million to deploy with construction taking 6 months or more — the mall turned to JMA and a CBRS network deployment, which Jacobs said will use nine radios and 13 antennas to cover the signs, which will be spread out at key traffic junctions. Total cost? About a half-million dollars. Total deployment time? About eight weeks, according to Jacobs. Jacobs said the system will also eventually be able to support mobile CBRS radios inside security vehicles for real time updates from the lots.
Verizon to cover all NFL stadiums with 5G… and lots of Wi-Fi
MSR was fortunate enough to get on the appointment schedule of Heidi Hemmer, Verizon’s vice president of technology. A few days after Verizon had publicly announced a spate of 5G deployments in NBA arenas, Hemmer doubled down on the carrier’s 5G commitment to NFL stadiums, saying the current list of 13 stadiums with some kind of Verizon 5G coverage would soon expand to the entire league.While hype is heavy around 5G — if you’re a football fan you’ve no doubt seen the Verizon TV commercial where Verizon’s technology development director Eric Nagy walks around various stadiums touting the service — Hemmer was clear that 5G is just part of a full-spectrum stadium wireless solution, one that will likely include 4G LTE as well as Wi-Fi well into the future.
While Verizon is clearly proud of its cutting-edge 5G deployments, the company is also probably the biggest provider of Wi-Fi networks in large stadiums, with many NFL and even some large colleges having Verizon-specific SSIDs for Verizon customers, usually as part of a sponsorship deal from Verizon. Verizon is also a big bankroller of distributed antenna system (DAS) deployments inside stadiums, sometimes acting as the neutral host and other times participating as a tenant on the in-venue cellular networks.
According to Hemmer, having as much connectivity as possible allows Verizon to provide the best possible experience for its customers. The eventual end goal, she said, would be a world where fans’ phones “dynamically” connect to whatever network is best suited for their needs, from Wi-Fi to 4G to 5G. Currently, many of the Verizon Wi-Fi deployments will automatically connect Verizon customers to Wi-Fi in a venue where they have previously logged on to the network.And while the millimeter-wave 5G deployments inside stadiums right now don’t come close to covering the full space of any venue (at the Denver Broncos’ Empower Field at Mile High, for instance, there are only 16 5G antennas in the building), they do provide a different level of connectivity, with much faster download speeds and less latency. Hemmer said those characteristics could spawn an entirely new class of services for fans like better instant-replay video or advanced statistics. While MSR hasn’t personally tested any 5G networks, the early word is that in some situations download speeds can be in the gigabit-per-second range.
“Speeds are important to our customers and 5G can really push up the fan experience,” Hemmer said.
New Boingo CEO bullish on venues business
Mobile World Congress was also MSR’s first chance to meet Mike Finley, who became Boingo’s CEO back in February. A former Qualcomm executive, Finley said that Boingo’s history of being a neutral-host provider for venues should continue to drive more business in that realm, especially as newer complex possibilities like CBRS and Wi-Fi 6 networks emerge.
“We are satisfying a need” that venues have for connectivity expertise, Finley said, especially when it comes to relationships with wireless carriers.
At MWC, Boingo was part of the CBRS Alliance’s multi-partner booth space promoting the OnGo brand for CBRS gear and services. In its space Boingo was showing its new converged virtualized core offering (which was using JMA’s XRAN product) with a live combined CBRS and Wi-Fi 6 network running side by side. A booth representative with an iPhone 11 device was able to quickly switch between the two networks, offering a glimpse at the potential future networking choices venues may be able to offer.
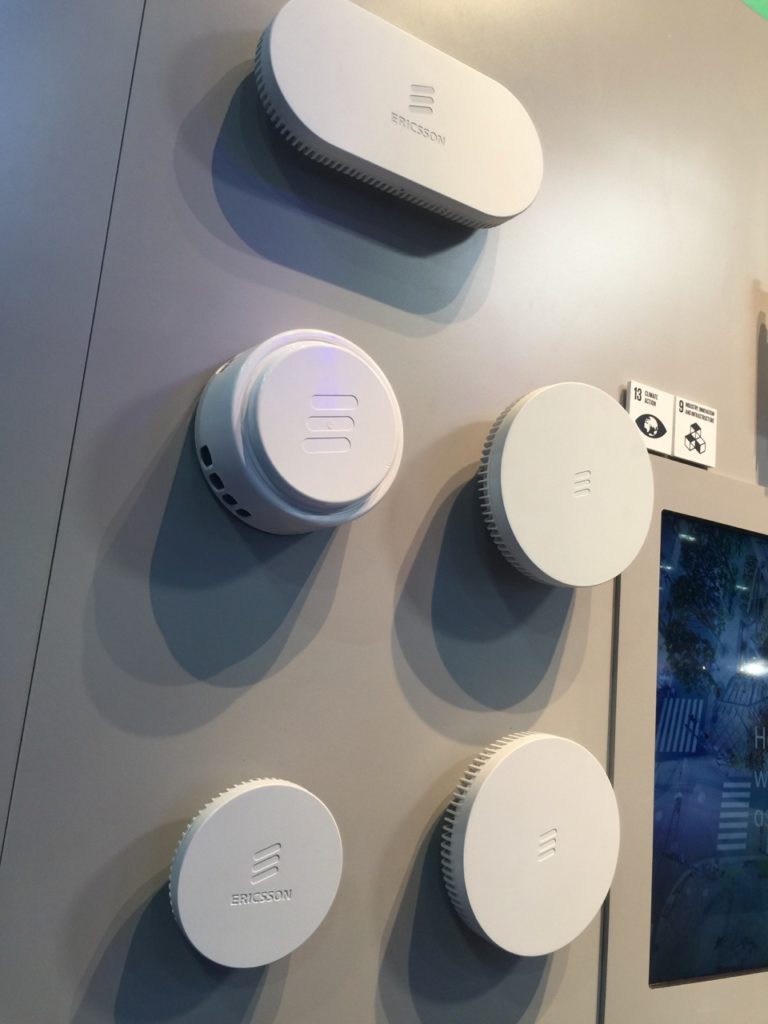
Ericsson Dots target stadiums, CBRS
In its large MWC booth, connectivity gear provider Ericsson had a special display for venue equipment, including a weather-hardened version of its Radio Dot System that Ericsson booth reps said should be appearing soon in some U.S. sporting venues. Ericsson was also showing some Dots that it said would support CBRS, a service Ericsson sees great promise for in venues.
Paul Challoner, Ericsson’s vice president for network product solutions, said it will be interesting to see whether or not venues will need to pursue licenses for CBRS spectrum when those are auctioned off next year, or whether venues will choose to use the unlicensed parts of the CBRS spectrum. Like others at the show, Challoner was excited about Apple’s decision to include support for CBRS bands in the iPhone 11 line — “it’s a fantastic boost for the CBRS ecosystem,” he said.
More MWC photos below!
Some of the Ericsson Dot radios designed for inside venue use
A prototype digital display kiosk from JMA, Intel and LG MRI, with space up top for CBRS gear
Another wireless-enabled display kiosk, this one in the Ericsson booth. Looks like wireless and digital displays are the next hot product.